
The three most typical application scenarios of Zigbee module ZM32
“The ZM32 series is a high-performance ZigBee module designed by ZLG Ligong Technology based on the Silicon Labs EFR32MG solution. In the previous section, we introduced the actual measurement and performance advantages of this module in detail. You can also review the previous evaluation articles.
“
The ZM32 series is a high-performance ZigBee module designed by ZLG Ligong Technology based on the Silicon Labs EFR32MG solution. In the previous section, we introduced the actual measurement and performance advantages of this module in detail. You can also review the previous evaluation articles:
“25 floors? ! ZigBee Hardcore Passing Through Buildings You Have Never Seen
“ZM32 in-depth analysis of -25 floors through the building actual measurement revealed”
“ZM32 in-depth analysis-we have done all the functions you want”
In the application cases of ZM32 series ZigBee modules, we have extracted the three most typical application scenarios:
l Multi-level routing cascading: For example, when ZigBee is used for networking in the smart street lamp industry, routing cascading is often used to extend the communication distance, so that the entire wireless network can cover several kilometers;
l Complex network topology: In some industries, the network topology is complex, such as the commercial lighting industry, requiring ZigBee nodes to complete networking in the fastest time, and to ensure that the nodes have a certain degree of stability and reliability (network self-healing) ability);
l Concurrent reporting: In a large-scale network, for example, the smart factory industry requires multi-point data collection, the probability and number of all nodes concurrency will increase, posing greater challenges to the processing capacity of the network;
In view of the above three situations, a detailed analysis is carried out in combination with the characteristics of the module.
1. Multi-level routing cascade-intelligent street lights
With the advent of the Internet of Things, urban traffic automation and intelligence requirements are comprehensively upgraded. The distance between street lamp nodes ranges from 20 to 200 meters. In each control system network, the number of street lamps under the gateway is controlled within 1,000. On-site construction requires simple and convenient operation.

Figure 1 Real view of street lights
Project plan: use industrial control board as the centralized controller of street light system, wide area network establishes connection with remote server center through 4G technology (gateway equipment), local area network uses ZigBee wireless network to control the scene lights, and at the same time receive street light status data returned by street light nodes .
l Street lamp node: Each street lamp has a ZM32 series ZigBee module, which is not only a node, but also a route, to form a communication network in a certain area;
l Gateway controller: The gateway controller can directly use the ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics industrial control host for edge computing, and control and data processing of street light nodes;
l Data transmission terminal: As the gateway controller is distributed in various areas and is usually far away from the server host, all street light data needs to be managed uniformly, so 4G DTU is used as a bridge between the local area network and the wide area network.
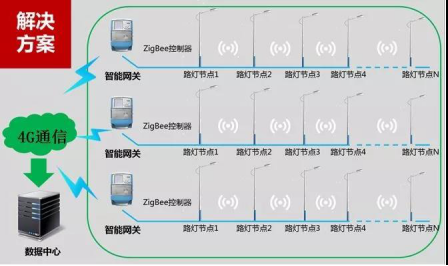
Figure 2 Project plan diagram
Each street light node is controlled by a ZM32 module. The ZM32 module can support multi-level routing and cascading to form a ZigBee network, and forward and transmit street light node data. We know that ZigBee communication efficiency will decrease as the number of routing stages increases, so routers must be laid out on demand. So, how many levels of routing layout can the ZM32 module support? What is the networking time and communication performance after multi-level routing is cascaded? The engineers of ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics conducted a multi-level routing cascade test on the ZM32 module.
In the indoor environment, the communication cascade test is performed, mainly recording the networking time under the cascading network structure and the communication performance between the coordinator and the routing device at the deepest level of the network to verify the multi-hop function of the module. The test results are as follows surface.
Table 1 Test results
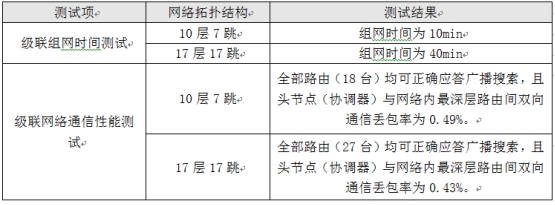
Note: The main purpose of this test is to verify the multi-hop, and the office space is limited, so the remote signal strength is adjusted to a critical state, so that each module is transmitted in turn to ensure the cascading effect. In actual use, the signal strength can be ensured by changing the installation position to avoid critical conditions.
In the actual space environment, when the RSSI reaches -92dBm, it is already close to the critical value of the receiving state. At this time, the communication stability is not high and it is very susceptible to interference. When the communication is interrupted due to interference, it will increase the packet loss rate and networking time. Therefore, the current test results may have certain errors. The detailed test plan can consult ZLG engineer.
2. Complex network topology-commercial lighting
Commercial lighting itself is a ready-made interconnection network, and then the introduction of Mesh network into it can provide commercial and industrial facilities with an innovative way to improve operational efficiency and support new business opportunities. Retailers will be able to provide in-store navigation and customized promotions; hospitals will be able to track patients and equipment; factories will be able to automate monitoring and maintenance; companies will be able to intelligently control lighting and room temperature, and monitor occupancy and safety. With its unparalleled universality, reliability and interoperability, Mesh network transforms smart lighting into a wireless connection platform.

Figure 3 Commercial lighting scene diagram
The ZM32 module uses the Mesh networking method for networking, and the characteristics of the wireless Mesh network are mainly ultra-long-distance transmission capabilities (wide network coverage) and self-repair capabilities. The following figure shows the topology of the Mesh network.
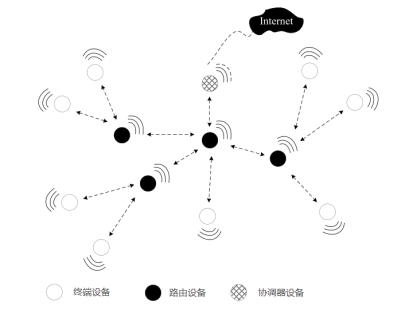
Figure 4 Mesh network topology
So, in a complex Mesh network, how stable is the ZM32 series of ZigBee modules? Similarly, ZLG engineers conducted a stability test on the ZM32 module. When conducting a large-scale ad hoc network, a continuous long-term test was performed under high-intensity data transmission to verify the stability and reliability of the ZM32 module. Through simulated network A certain key node is permanently damaged, and the self-healing time of the network is tested. The test is mainly divided into terminal equipment networking test and full routing networking test. For detailed test plans, please consult ZLG engineers. The test conclusions are as follows:
Ø Terminal networking test:
l 245 devices can be successfully concurrently connected to the network within 1 minute (a total of 240 terminals + 5 routers in the test);
l When key nodes are powered off, the network self-healing time is about 7 minutes (if there are fewer numbers in the network, the self-healing time will be shorter);
l Broadcast control can respond in time;
l In dormant and non-dormant states, it can report stably and regularly.
The above is the networking time using ad hoc networking. If the configuration networking mode is adopted, the networking time can be shortened.
Ø Full routing network test:
l A network composed of 101 devices can be successfully concurrently connected to the network within 32 minutes (a total of 101 routing devices were tested);
l In a network composed of 101 devices, the key nodes are powered off, and the network self-healing time is about 15s (if the number in the network is small, the network self-healing time will be shorter);
l Broadcast control can respond in time;
l 101 routers can report stably and regularly when they are not in sleep state.
The above is the networking time using ad hoc networking. If the configuration networking mode is adopted, the networking time can be shortened.
3. Concurrent reporting-smart factory
The development of the Internet of Things technology has accelerated the transformation and upgrading of Industry 4.0. A series of industries have begun to transform to information management. The transformation from traditional factories to smart factories will inevitably become a “wave” in the world’s manufacturing industry in the future, and traditional factories are rapidly realized The method of role conversion is to realize the interconnection and intercommunication between devices.

Figure 5 Scene diagram of smart factory
Take the textile industry, one of China’s top ten pillar industries, for example. At present, the automatic monitoring of loom operation generally uses a single-chip monitoring system or a single-host distributed monitoring system based on the RS-485 bus. Some looms also use a CAN bus monitoring system. However, these loom operation monitoring systems have shortcomings such as high cost, complex system structure, poor anti-interference performance, and difficulty in system maintenance.
Compared with RS-485 bus and CAN bus, ZigBee technology has obvious advantages in terms of real-time performance, anti-interference and reliability, as well as system cost and scalability, except for the shorter communication distance. At the same time, in terms of system wiring, because ZigBee adopts a wireless method, it can solve the problem of complicated wiring.
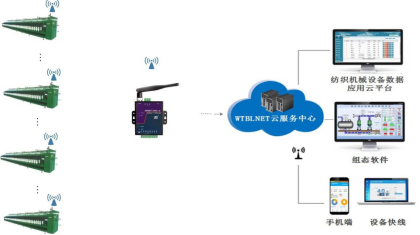
Figure 6 ZigBee wireless solution
However, in a large-scale network such as a smart factory, the probability and number of concurrency of all nodes will increase, posing greater challenges to the processing capabilities of the network. Therefore, ZLG R&D engineers conducted a concurrent test on ZM32 to test the concurrent processing capability of ZM32. The test is mainly divided into full terminal concurrent reporting and full routing concurrent reporting. For detailed test schemes, please consult ZLG engineers. The test conclusions are as follows:
Ø Concurrent reporting for all terminals:
l The maximum concurrent number is 62, and the reporting time is about 3.5s;
l When the number of transmitted bytes exceeds the maximum load of a single radio frame (74 bytes), the maximum number of concurrent transmissions is 20, and the reporting time is about 3.5s.
The above test serial port is only sent once, if the user increases the retransmission, the number of concurrency will increase.
Ø Concurrent reporting for all routes:
l In the full-route concurrent reporting test, the number of transmitted bytes is less than the maximum load of a single radio frame (74 bytes), the maximum concurrent number is about 30 units, and the reporting time is about 3.5s.
The above test serial port is only sent once, if the user increases the retransmission, the number of concurrency will increase.
The Links: 7MBR100VX120-51 6MBI450V-170



